Outokumpu 4762
| 牌号 | Outokumpu 4762 |
| 厂家 | Outokumpu |
| 分类 | Steel |
| 介绍 | The high temperature (HT) ferritic stainless steels complement Outokumpu Stainless austenitic heat and creep portfolio. The main alloying element in the ferritic grades is chromium. Its positive effect on the scaling resistance is enhanced by silicon and aluminium. The two lower alloyed grades are best suited for temperatures between 550°C and 850°C, at which most HT austenitic stainless steels are prone to form brittle phases. The higher alloyed ones are applied at temperatures up to 1150°C and show excellent resistance against reducing sulphur attacks and molten metals. Due to their ferritic structure, the ferritic steels show lower strength at temperatures exceeding 600°C, but are more resistant to thermal shocks than HT austenitic stainless steels. With the thermal conductivity higher and the thermal expansion lower than the respective values for austenitic steels, equal thermal shocks will result in lower thermal stresses in the ferritic material. In these terms, ferrites allow greater tolerances for design and operation. 4762 - with the highest chromium content- is the most resistant to reducing sulphurous gases. It is susceptible to the same embrittlement phenomena as 4742 whilst s-phase forms during long exposures in the range 600°C to 800°C. |
| Outokumpu 产品展示 | 种类 |
|---|---|
| Outokumpu 4845 | Steel |
| Crofer® 1925 hMo - alloy 926 | Steel |
| Outokumpu 4401 | Steel |
| Outokumpu 1.4509 | Steel |
| Outokumpu LDX 2101® | Steel |
| Outokumpu 4948 | Steel |
| Outokumpu 4713 | Steel |
| Outokumpu 4724 | Steel |
| Outokumpu 654 SMO® | Steel |
| Outokumpu 153 MA™ | Steel |
订购说明
上海松翰塑化科技有限公司订货流程
【订购导引】
我司所销售所有产品均为原厂原包,均可提供相关资料报告(如:物性表,MSDS报告,UL报告,COA报告,SGS报告,FDA等)!
如您需要提前了解原料产品的相关性能或是需要原料产品的相关报告,请您通过电话或是客服QQ与我联系!
【物流说明】
自接到贵司订购单24小时内发货,珠三角,长三角,北京,天津均支持代收货款。货物送达后,请第一时间检查外包装,如发现物流过程中出现大量包装损坏及原料外漏的,请让物流人员出具证明并保存,并在24小时内与我司客服部取得联系。
【订购流程】
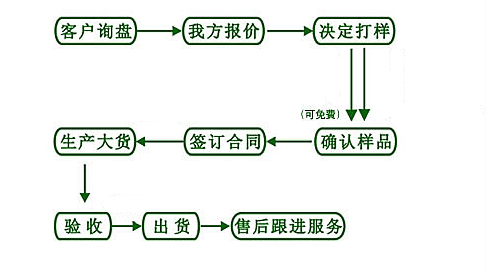
【退换货处理】
退货:
依照中华人民共和国消费者保护法规,在您收到货品7天内,若发现您收到的商品有瑕疵或损坏,您可以要求退货,请主动与本公
司联络,敝公司接到您的商品之后,会将您的购物金额全额退回。
换货:
若您收到的商品有瑕疵或损坏,请您于7天内与本公司联络,本公司有专人处理换货事宜。
我司所销售所有产品均为原厂原包,均可提供相关资料报告(如:物性表,MSDS报告,UL报告,COA报告,SGS报告,FDA等)!
如您需要提前了解原料产品的相关性能或是需要原料产品的相关报告,请您通过电话或是客服QQ与我联系!
【物流说明】
自接到贵司订购单24小时内发货,珠三角,长三角,北京,天津均支持代收货款。货物送达后,请第一时间检查外包装,如发现物流过程中出现大量包装损坏及原料外漏的,请让物流人员出具证明并保存,并在24小时内与我司客服部取得联系。
【订购流程】

【退换货处理】
退货:
依照中华人民共和国消费者保护法规,在您收到货品7天内,若发现您收到的商品有瑕疵或损坏,您可以要求退货,请主动与本公
司联络,敝公司接到您的商品之后,会将您的购物金额全额退回。
换货:
若您收到的商品有瑕疵或损坏,请您于7天内与本公司联络,本公司有专人处理换货事宜。